When it comes to dental lab restorations, choosing the right material is crucial for achieving durability, aesthetics, and patient satisfaction. Two of the most popular materials used today are zirconia and lithium disilicate. Both offer unique advantages, but understanding their differences will help you select the ideal material for your cases. In this post, we’ll break down their properties, benefits, and ideal applications.
Zirconia Dental Material
Overview:
Zirconia (zirconium dioxide) has become a go-to material for dental restorations, thanks to its exceptional strength and durability. Often referred to as “ceramic steel,” zirconia can withstand high chewing forces, making it ideal for long-term restorations.
Key Benefits of Zirconia:
- Strength and Durability
- Zirconia boasts a flexural strength of over 1,000 MPa, making it resistant to fractures and wear.
- Ideal for Posterior Restorations
- Its strength makes zirconia perfect for crowns, bridges, and implant-supported restorations in areas with high occlusal forces.
- Biocompatibility
- Zirconia is non-toxic and highly biocompatible, reducing the risk of irritation and inflammation.
- Monolithic and Layered Options
- Monolithic zirconia offers maximum strength, while layered zirconia combines strength with improved aesthetics.
Best Applications for Zirconia:
- Posterior crowns and bridges
- Full-arch implant restorations
- Bruxism cases requiring high durability
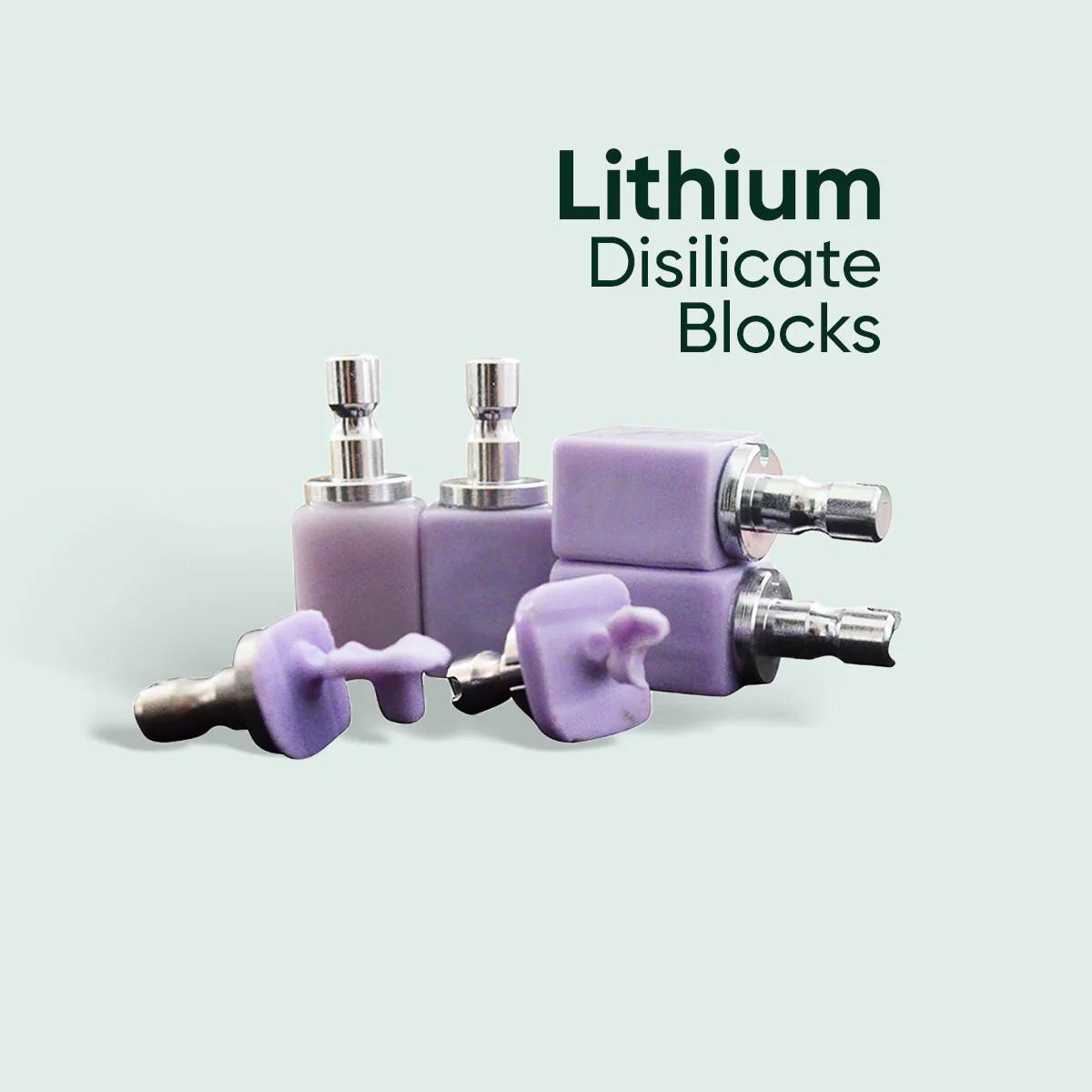
Lithium Disilicate
Overview:
Lithium disilicate is a glass-ceramic material known for its superior translucency and natural-looking aesthetics. With a flexural strength of around 400 MPa, it strikes a balance between beauty and durability.
Key Benefits of Lithium Disilicate:
- Superior Aesthetics
- Lithium disilicate provides excellent translucency and a life-like appearance, making it ideal for anterior restorations.
- Adequate Strength
- While not as strong as zirconia, it offers sufficient durability for single-unit restorations.
- Minimal Preparation
- Its strength allows for minimal tooth reduction, preserving natural tooth structure.
- Bondability
- Lithium disilicate is highly adhesive, ensuring strong bonding when used with resin cements.
Best Applications for Lithium Disilicate:
- Anterior crowns and veneers
- Inlays and onlays
- Single-unit restorations in low-load areas
Zirconia vs. Lithium Disilicate: A Quick Comparison
| Property | Zirconia | Lithium Disilicate |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | > 1,000 MPa (High) | ~400 MPa (Moderate) |
| Aesthetics | Good (Improved with layering) | Excellent (Superior translucency) |
| Biocompatibility | Highly biocompatible | Biocompatible |
| Best Applications | Posterior crowns, bridges, implants | Anterior crowns, veneers, inlays |
| Bonding Requirement | Minimal | Requires adhesive bonding |
How to Choose the Right Material for Dental Lab Restorations
- For Strength and Functionality: Choose zirconia for posterior restorations or full-arch cases where strength and durability are critical.
- For Aesthetics and Natural Look: Opt for lithium disilicate for anterior crowns and veneers where esthetic results are a top priority.
- Patient-Specific Needs: Consider factors such as bruxism, load-bearing areas, and patient esthetic expectations to guide your decision.


Conclusion
Both zirconia and lithium disilicate are excellent materials for dental restorations, each serving different purposes in the dental lab workflow. By understanding their strengths, limitations, and ideal applications, dental technicians can deliver restorations that meet both functional and esthetic demands.
Explore our online store for premium zirconia and lithium disilicate materials to enhance your lab’s capabilities and deliver exceptional results to your clients.